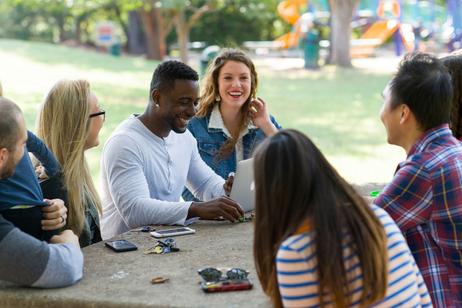Community College Success Stories Parents Should See
Community colleges often carry a misperception: that they are fallback options—or short-term stepping stones with limited outcomes. Yet, beneath the stereotypes lie rich stories of transformation, resilience, and generational change. For parents guiding teens or adult learners, the success stories of community college alumni offer powerful lessons and real-world proof of what’s possible.
This article highlights current (2025-2026) examples and themes, backed by data and expert insights, to help parents see community college not as second best—but as a viable pathway to long-term success.
Why Parents Should Pay Attention to Community College Paths
1. Cost-efficient and flexible
Community colleges generally offer far lower tuition than four-year institutions, making them attractive for families mindful of debt. They also offer high flexibility—night classes, hybrid formats, and part-time schedules—making them ideal for working students, parents, or those needing to balance other commitments.
2. Transfer and degree pathways
Many community colleges offer guaranteed or guided transfer agreements with four-year universities. These articulation agreements smooth the transition to bachelor's degree programs. Some also offer “university center” models so students can complete a four-year degree while staying on the community college campus. For example, Macomb Community College supports degree completion through its University Center model. (Wikipedia)
3. Career and technical education
Beyond transfer, community colleges often provide strong career and technical education (CTE). Alumni can emerge with industry-ready skills or certifications, ready to